

Show mac-address-table address *mac-address* show mac address-table address *mac-address* Depending on the Cisco platform, sometimes the command is listed in either form. Now issue one of the following commands (where mac-address is the hardware address from previous step). Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface The output should look similar to below, and give you the mac-address of the device (I've highlighted the mac-address below in bold). Log into the switch and issue the following command (where ipaddress is the ip address of the host you are trying to locate: show ip arp *ipaddress* In either case, the commands are the same, just run on two different boxes for the layer 2 switch. However on a layer 2 switch, you have to log into both the switch and whatever device is doing the routing to locate the port. On a layer 3 switch, the port can be found by using a few simple commands on the device. That is to say, is the switch only switching and relaying traffic on to a different device for routing, or, is it doing the routing decisions itself via SVIs (switched virtual interfaces). If you provide incorrect password, the command would fail with the error message “ Logon failure: unknown user name or bad password.The answer depends on whether the switch is a Layer 2 or a Layer 3 switch. If you try this for a Linux machine you would get the error “ The RPC server is unavailable.” Using getmac command we can retrieve the mac addresses of the machines running windows OS only. You will be prompted to enter the password and the command execution will take place after that. If you do not want to specify the password, you can skip /p parameter. Just run the command getmac to get the mac addresses. It works on XP, Vista, Windows 7, Server 2003 and Server 2008 operating systems. Below are few examples on how to use this command.
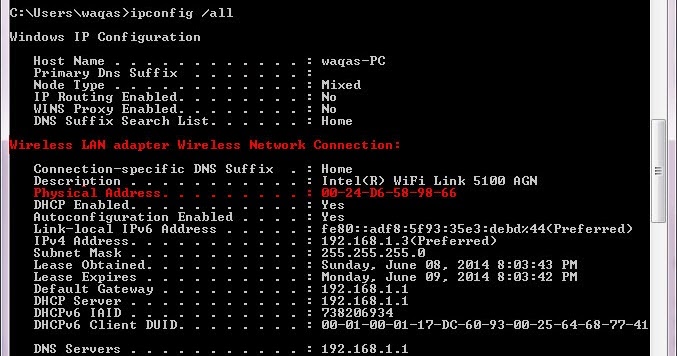
This can be used to get mac address for remote computers also.


We can find mac address (physical address) of a computer using the command ‘ getmac‘.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
